Today, most people know how to use a web browser. So, this section focuses on describing the characteristics of Firefox. It also tells you how to install some of the more popular plugins.
Launch Firefox by selecting + → from the main menu.
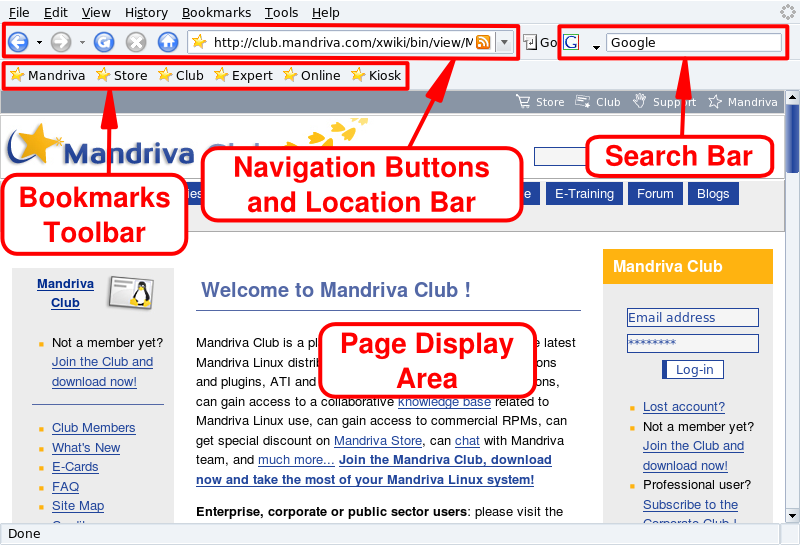
The main components of Firefox's interface are:
Page Display Area. Where the contents of the pages you browse are displayed.
Navigation Buttons and Location Bar. Buttons allowing you to move
around pages you visit: go back, go forward; refresh a page; stop
loading page elements; and go to your home page. The
location bar is where you enter a web site's URL (or a local file
using file:// as the protocol part of the
URL).
Bookmarks Toolbar. You can hide or display the bookmark bar, and add additional buttons to it. To do so, simply select → → and select the items you want to add, and click .
Search Bar. Located at the upper-right corner, it allows you to perform web searches, dictionary searches, and others.
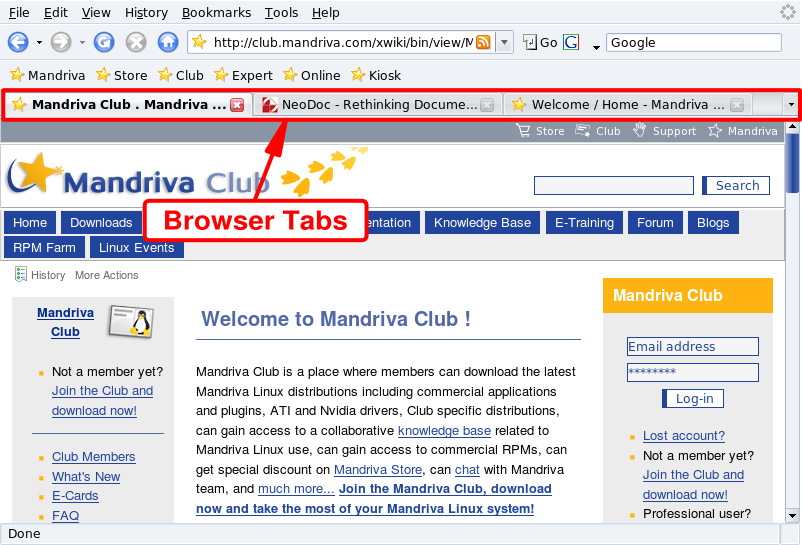
One of Firefox's most convenient features is the ability to browse many websites at the same time, without being confused with all the open windows. Each website is opened in a new tab. This is called “tabbed browsing”.
To open a new tab, click → . To close a tab, right-click on the tab, and select Close Tab. You can also click on the cross located at the right of the tab.
![[Tip]](images/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
To quickly open new tabs, simply press Ctrl-T as many times as you want tabs. Pressing Ctrl-W closes the currently open tab. |
Firefox enables you to manage tabs easily. You can choose to close, refresh, mark-up all tabs on the fly, or just the one currently displayed. To do so, right-click on a tab, then select the option you want.
You can also move tabs. Click on a tab, hold the mouse button down and drag it where you want. When you see a little purple downward-pointing arrow, you can drop the tab to its new location on the tab browsing bar.
If you want to duplicate a tab, “grab” the tab's URL (when rolling your mouse over the icon before the URL: a little hand pointer appears) in the location bar, drag-and-drop it onto an empty tab.
Firefox has a built-in search bar which allows you to search the web using the most popular search engines. To perform a search, type the text to be searched for, select the search engine (using the arrow and icon at the left of the search bar) and press the Enter key. Search results are shown in the Page Display Area.
Plugins are
programs which let your browser handle content other than HTML
and graphics, such as animations, streaming audio, Javatm applets, and
so on. Firefox's plugins are stored in the
/usr/lib/mozilla/plugins directory and
installing plugins requires root privileges.
![[Tip]](images/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
Entering
|
We look at the procedures to install Javatm and Flash® plugins. If you own a commercial version of Mandriva Linux, installation is greatly simplified and all the required packages are on the provided media. See Chapter 7, Package Management, for information on how to install RPM packages.
![[Note]](images/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
If you have a Mandriva Club user name and password, you may be able to install even newer versions of the software mentioned here. |
You can get the Java plugin on the Java Plug-in Home Page. Follow the links to J2SEtm (Java 2, Standard Edition) and download the JRE for Linux. Choose the RPM file for the Linux Platform, make it executable once the download is finished (chmod 700 jre*.rpm.bin) and execute it. Accept the license and a “real” RPM will be created.
You can retrieve the Flash plugin on the Adobe® web site. Follow the link to the Flash Player and download and install the RPM. Test the plugin by opening the Flash web site URL in the browser.